Corporations can use a variety of different depreciation methods such as double declining balance and sum-of-years-digits to lower taxes in the early years. Let’s look at the example of an owner of a fleet of trucks whose equipment depreciated over the tax year. Depreciation is a deductible expense, depreciation tax shield formula and a portion of the depreciated amount can therefore lessen the owner’s overall tax burden. Assuming depreciation totaled $20,000 and a tax rate of 10%, the truck owner can subtract $2,000 from his total taxable income. Using illegal methods to avoid tax payment is known as tax evasion.

Enterprise Value vs Equity Value – Ultimate Guide (

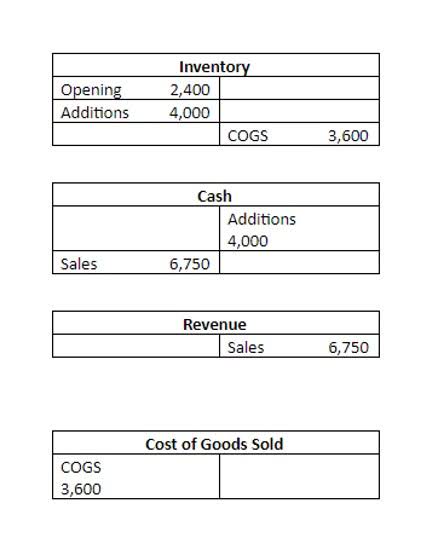
There are several different depreciation methods and each has its own calculation. The most common method is the straight-line method, which basically involves expensing the same amount for each accounting period. The straight-line method is calculated by subtracting the salvage value from the asset’s purchase price and then dividing the resulting figure by the projected useful life of the asset.
Types of Tax Shields
Private Equity Funds typically use large amounts of Debt to fund acquisitions. The Debt used in the purchase creates Interest Expense that reduces the acquired Company’s Tax bill. Below we have also laid out the Depreciation Tax Shield calculations using the Sum of Years Digits approach. Below are the Depreciation Tax Shield calculations using the Straight-Line approach. Below, we take a look at an example of how a change in the Depreciation method can have an impact on Cash Flow (and thus Valuation). As you can see from the above calculation, the Depreciation Tax Savings as the expense increases.
Key Considerations When Adding Back a Tax Shield
Depreciation using the straight-line method reflects the consumption of the asset over time and is calculated by subtracting the salvage value from the asset’s purchase price. That figure is then divided by the projected useful life of the asset. Where we is the weight of equity, ke is the cost of equity, wd is the weight of debt, kd is the pre-tax cost of debt (i.e. its yield to maturity) and t is the tax rate. Implementing an effective tax shield strategy can help increase the total value of a business since it lowers tax liability.
- If you don’t report every element of your income—including bonuses paid by your employer and tips—then you are guilty of tax evasion.
- Many middle-class homeowners opt to deduct their mortgage expenses, thus shielding some of their income from taxes.
- Therefore, you might conclude that taking on debt has a tax benefit as the interest may be deducted from your income.
- A tax shield refers to tax deductions that an individual or business can take to lower their taxable income.
- When filing your taxes, ensure you are taking these deductions so that you can save money when tax season arrives.
Even though the APV method is a bit complex, it is more flexible because it allows us to factor-in the risk inherent in admissibility of interest tax shield. The factor of (1-t) reduces the debt component which results in a lower WACC which in turn results in a higher present value of net cash flows. Interest expenses on certain debts can be tax-deductible, which can make the entire process of debt funding much easier and cheaper for a business. This works in the opposite way to dividend payments, which are not tax-deductible.
Giving to charitable organizations can shield you from a hefty sum of income taxes. Typically, you can deduct cash donations equal to 60% of your AGI and asset donations equal to 30% of your AGI. In addition, capital gains taxes receive a 20% deduction for the donated asset. It offers businesses a way to recover the cost of an eligible asset by writing off the expense over the course of its useful life. A business can expect a big impact on its profits if it doesn’t account for the depreciation of its assets.
The tax shield concept may not apply in some government jurisdictions where depreciation is not allowed as a tax deduction. It should be noted that regardless of what depreciation method is used the total expense will be the same over the life of the asset. Thus, the benefit comes from the time value of money and pushing tax expenses out as far as possible.
- Donating to charity might lessen one’s tax liabilities, much as the tax break provided as reimbursement for medical expenditures.
- The “best method” is the one appropriate for your business and situation.
- Mr. Arora is an experienced private equity investment professional, with experience working across multiple markets.
- There is a real-time value of money saved since tax is a cash charge, but depreciation is a non-cash expense.
- A tax shield is a fully legal strategy that taxpayers can use to reduce their tax burden and should not be confused with tax evasion.
The Tax Impact of Depreciation
The Interest Payments are typically tax-deductible, which lowers the Company’s tax bill. First, when a Company borrows money (or ‘Principal’) from a Lender, they typically agree to repay the borrowed dollars in the future. As you can see, the Taxes paid in the early years are far lower with the Accelerated Depreciation approach (vs. Straight-Line). As an alternative to the Straight-Line approach, we can use an ‘Accelerated Depreciation’ method like the Sum of Year’s Digits (‘SYD’). Taxes play a crucial role in helping governments finance a range of projects, including infrastructure, wars, and public works.
- A tax shield represents a reduction in income taxes which occurs when tax laws allow an expense such as depreciation or interest as a deduction from taxable income.
- Since depreciation expense is tax-deductible, companies generally prefer to maximize depreciation expenses as quickly as they can on their tax filings.
- Tax shields allow taxpayers to reduce the amount of taxes owed by lowering their taxable income.
- SmartAsset Advisors, LLC (“SmartAsset”), a wholly owned subsidiary of Financial Insight Technology, is registered with the U.S.
- Where CF is the after-tax operating cash flow, CI is the pre-tax cash inflow, CO is pre-tax cash outflow, t is the tax rate and D is the depreciation expense.
- Deductions for mortgage interest, charity donations, medical costs, and depreciation are a few examples.
Leave a Reply